(Translation: Zelelaem Aberra Tesfa)
http://www.zelealemaberra.com/?page_id=388


Sof Umar Wall, Bale Oromia (Ancient and magnificent past and present)
Parts of ancient kemetic (Kushitic), Egyptian, material culture (fashion accessories), courtesy of British Museum sources
Traditionally, Oromo women wear necklaces with telsum amulets, triangular and crescent shaped pendants protect from the evil eye and attract the power of the moon or to improve fertility.
Oromia: The continuity of farming in Oromo society from ancient Kemetic (Kushitic) to present Oromia
Ancient Oromo culture, Irreechaa from the time before the Pyramid
As some indeed suspect, that the science which we see at the dawn of recorded history, was not science at its dawn, but represents the remnants of the science of some great and as yet untraced civilisation. Where, however, is the seat of that civilisation to be located? (J. W. S. Sewell, 1942)
Conquest and dominations are social phenomenon as are dying elsewhere will die in Oromia (Author’s Remark).
JEL: O5, D2
Oromia: Untwist the Twisted History
The topic is about Oromia’s location in space and allocation in humanity and society. It is concerned with Oromia’s physical position in terms of geography and relational to issues of economic conditions, social justices, cultural values, political history and destiny. Civilisation, Colonisation and Underdevelopment are presented in historical and geo-political perspectives. They capture both the space and time perceptions. They are also representing the economic and social conditions and positions. The portrayal we procure the present of the Oromo nation, the core of the Cush (Cushite/ Kemet)/Ham (Hamite), the children of Noah, in North & East Africa in past age from the phantom of the Solomonic dynasty, the history thought in Abyssinian high schools, their text books and elsewhere in the invaders’ literature, abusive literary and oral discourses is that they were savages and that, though Abyssinians and Europeans overrun their lands and have made mere subjects of them, they have been in a way, bestowing a great favour on them, since they have brought to them the benisons of Christian Enlightenment. With objective analysis, however, this paper obliterates and unmakes that inaccurate illustration, wanton falsifications, immorality, intellectual swindle, sham, mischievous tales, the bent and the parable of human reductionism. Hence, it is the step to delineate an authentic portrait of a human heritage, which is infinitely rich, beautiful, colourful, and varied in the retrograde of orthodox misconceptions. The paper is not only a disinclination itself but also a call for and a provocation of the new generation of historians to critically scrutinise and reinvestigate the orthodox approaches to the Oromo history and then to expose a large number of abusive scholarship authorities on the Oromo and Cushitic studies and it detects that they do not really know the intensity and profoundness of the history of these black African people and nations and the performance these Africans registered in the process of creating, making and shaping the prime civilisations of human societies. The study acknowledges and advances a strict contest to an orthodox scholarship’s rendition of Egypt as a white civilisation, which arose during the nineteenth century to fortify and intensify European imperialism and racism. Depending on massive evidences from concerned intellectual works from linguistic to archaeology, from history to philosophy, the study authenticates that Egypt was a Cushitic civilisation and that Cushite civilisation was the authentic offspring of the splendid Upper Nile/ Oromian legacy. The Greek civilisation, which has been long unveiled as the birthplace of Western philosophy and thought, owes its roots to the Cushites thoughts and achievements. The original works of Asfaw Beyene (1992) and F. Demie (in Oromia Quarterly, 1998 & 2000) are giving motivations and also greatly acknowledged. The study also expresses that radical thinkers and multi-genius African historians such as Diop (1991) have not given due attention to the epic centre of Cushitic civilisation, Oromia, the land after and Eastern and South Eastern to Nubia, pre-Aksum central Cush, Aksumite Cush and Cushites civilisation southern to Aksum, etc. The method of enquiry is qualitative and the eclectics of formal and the informal sources, rigorous, casual and careful scholarship argument. Oral history and written documents on history, economy, sociology, archaeology, geography, cosmology and anthropology are based on as references. The paper studies the Oromo history and civilisation in horizontal approach and challenges the reductionist and Ethiopianist (colonialist, racist) vertical approach (topsy-turvy, cookkoo). It goes beyond the Oromo Oral sources (burqaa mit-katabbii) and Africanist recorded studies and western civilisational studies. The approach is to magnify, illuminate and clarify the originality of humanity and civilisation to this magnificent Cushitic (African) beauty. The Origin of Humanity When and where did human life first surface on our cosmos? Who contrived the original and prime human culture and civilisation? Ancient Egyptians contended that it was in their homeland, the oldest in the world, the God modelled the first of all human beings out of a handful of ooze soddened by the vivacity of the life giving sanctified and blessed water, the Nile (see, Jackson, 1995). “The ancient Egyptians called the river Ar or Aur (Coptic: Iaro), “Black,” in allusion to the colour of the sediments carried by the river when it is in flood. Nile mud is black enough to have given the land itself its oldest name, Kem or Kemi, which also means “black” and signifies darkness. In The Odyssey, the epic poem written by the Greek poet Homer (7th century bce), Aigyptos is the name of the Nile (masculine) as well as the country of Egypt (feminine) through which it flows. The Nile in Egypt and Sudan is now called Al-Nīl, Al-Baḥr, and Baḥr Al-Nīl or Nahr Al-Nīl.”http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/415347/Nile-River Ar or Aur (Coptic: Iaro) is Booruu in modern Afaan Oromo which means turbid in English translations. Lagdi Nayili jedhamee amma waamamu maqaan kun kan akkanatti moggaasameefi, bowwaa jechuudha. Warri kushii, warri biyyaa, waarri durii laga isaanii Aur (Ooruu) jedhanii waamu. Afaan Oromoo amma uni dubbannuutti booruu jechuudha. Booruu (turbid) jechuuni gurri’aacha (Kami) jechuu miti. Booruu (Ooruu, Aur) jechuun kan taliila hin taane kan hin calaliini jechuudha. Dameen laga kanaa kan Moromor (dhidheessa) irraa maddu galaana biroo itti burqan dabalatee biyyoo loolan haramaniin waan booraweef. kaartumitti yoo damee isa (isa taliila) garba Viktooriyaati karaa Ugaanda dhufutti makamu kanasi booressee misiriitti godaana. Dameen Garba Viktooriyaati dhufu iyyuu adii (white) jedhamee mogga’uuni irra hin turre. Bishaani adiini hin jiru. Bishaani hin boora’iini bishaan taliila. Bishaani taliilatu bishaan guri’aacha. Inni ‘Blue’ jedhanisi ‘Blue’ mitti. Bishaan taliilatu, gurri’aacha ‘Blue’ dha. ‘Blue Nile’ jechuu irra ‘Brown’ Nile (Mormor Booruu, Ar, Aur) yoo jedhani ille itti dhiyaata. The word (Africa) Afrika itself derived from kemetic (Oromo) language. In Oromo, one of the ancient black people (kemet), Afur means four. Ka (Qa, Waqa) means god. Afrika Means the four children of god. It describes the four sub groups of kemet people. Such type of naming system is very common in Oromo even today such as Afran Qallo, Shanan Gibee, Salgan Boorana, Macca Shan, Jimma Afur, Sadan Soddoo, etc. For other theories in this topic please refer to http://atlantablackstar.com/2014/09/23/9-theories-africa-got-name/
One of the oldest Cushites histories to account for the origin and early development of man and his culture survives in a Greek version of the thesis advanced by the ancient Cushites, Oromians and the rest. This marvellous people paraded in golden times in the region called Kush (Punt) in the Hebrew Scriptures and stamped on the present-day upper Nile Oromia (see, Jackson, 1995). Diodorus Siculus, wrote that the Cushites were of the opinion that their country was not only the birthplace of human race and the cradle land of the world’s earliest civilisation, but, indeed, the primal Eden where living things first appeared on Earth, as reported by the Scriptures. Thus, Diodorus was the first European to focus attention on the Cushites asseveration that Upper Nile (Oromia) is the cradle land of world’s earliest civilisation, the original Eden of the human race. Whether by almighty (God) or nature/ evolution (Darwin’s natural selection and survival of the fittest), Oromia was not only the birth place of man himself (e.g., Lucy) but also for many hundred years thereafter is in the vanguard of all world progress (see Diop, 1991 in his African Civilisation; Martin Bernal, 1987). These are also authenticated by the present archaeological inferences in Oromo tropical fields and rivers valleys. The original natives of Egypt, both in old and in the latter ages of development, were Cushite and there is every raison d’être for the discourse that the earliest settlers came from upper Nile Oromia. The original homeland of the Oromians and other Cushites including Chadic, Berber, Egyptian, Beja, Central Cushitic, East Cushitic, South Cushitic, Omotic and Nilotic was the present day upper Nile Oromia. It was from the original Oromo (Madda Walaabu) that the rest of humanity descended diffused to other parts of the world. This can be understood in the analogue of the diffusion of two Oromo families (Borana and Barentuma). While those who expanded to other regions latter taken new family names like Macha, Tulama, Karayyu, etc and those who stayed in original place kept the original name such as Borana. In terms of linguistic, like most scholars, we believe that it is impossible to judge between the theories of monogenesis and polygenesis for human, though the inclination is towards the former. On the other hand, recent work by a small but increasing number of scholars has convinced us that there is a genetic relationship between European, Asian, and African and Cushite languages. A language family originates from a single dialect, proto Cushitic/ Oromo. From such language and culture that must have broken up into Africa, Asiatic, and European and within them a very long time a go. Professor Bernal (1987, in Black Athena, p. 11) confirmed that the unchallenged originality of Oromians and other Cushites nativity to the region and put forward that the latest possibility for initial language break up would be the Mousterian period, 50- 30,000 years Before the Present (BP), however, it may well have much earlier. He further observed that the expansion and proliferation of Cushitic and other Afroasiatic as the promulgation of a culture long pioneered in the East African Rift valley (South Eastern Oromian) at the end of the last Ice Age in the 10th and 9th millennia BC. According to Bernal (1987, p.11) the polar ice caps caged the water within itself, which was during the Ice ages, thus water was significantly less than it is nowadays. He reports that the Sahara and Arabian deserts were even bigger and more inhospitable then than they are presently. In the centuries that ensued, with the rise of heat and increase in the rainfall, greatly the regions became savannah, into which adjoining peoples voyaged. The most successful of these were, the speakers of Proto-Afroasiatic from upper Nile Oromia. Bernal further confirmed that these people not only possessed flourishing and effective skills and techniques of hippopotamus hunting with harpoons but also had domesticated cattle and food crops. The following is quoted from Black Athena: ‘Going through the savannah, the Chadic speakers renched lake Chad, the Berbers, the Maghreb, and the Proto-Egyptians, upper Egypt…. With long-term desiccation of the Sahara during the 7th and 6th millennia BC, there were movements into the Egyptian Nile Valley from the west and east as well as from the Sudan. … A similar migration took place from the Arabian savannah into lower Mesopotamia ‘(Bernal, pp.11-12).
The Origin of Civilization
There are many things in the manners and customs and religions of the historic Egyptians that suggest that the original home of their human ancestors was in the Upper Nile region and the biblical land of Punt/ Kush (Cush) Or Oromia which include the present day of Cushitic North and East of Africa. Hence, historical records showed that the antiquity of upper Nile Cushitic Oromian civilisation had a direct link with the civilisation of ancient Egypt, Babylonian and Greece. Hence, the Egyptian and Babylonian civilisations are part and parcel of the entire Cushite civilisation. As it is described above, there is wide understanding that Cushites = Egyptians + Babylon + Oromo+ Agau + Somalis + Afars + Sidama + Neolithic Cush + other Cush. There is also an understanding that all the Cushites are branched out (descended) from their original father Oromo which can be described as Oromo = Noah=Ham= Cush= Egyptian + Bablyon+ Agau + Somali + Afar + Sidama + Neolithic Cush + other Cush. Boran and Barentuma, the two senior children and brothers were not the only children of the Oromo. Sidama, Somali, Agau, Afar and the others were children of the big family. Wolayita and the Nilotics were among the extended family and generations of the Cushite. As a hydro-tower of Africa, the present Oromia is naturally gifted and the source of Great African rivers and hosts the bank and valleys of the greatest and oldest civilisations such as Nile (Abbaya), Baro (Sobat), Gibe, Wabe, Dhidhesa, Ganale, Wabi-shebele, Omo, and Awash among others. Oromian tropical land, equatorial forest and Savannah have been the most hospitable ecology on the earth and conducive environment to life and all forms of human economic and social practices. According to Clarke (1995), many of the leading antiquarians of the time, based largely on the strength of what the classical authors, particularly Diodorus Siculus and Stephanus of Nabatea (Byzantium after Roman colonisation and Christianisation), had to say on the matter, were exponents of the vista that the Cushite, the ancient race in Africa, the Near East and the Middle East, or at any rate, the black people of remote antiquity were the earliest of all civilised peoples and that the first civilised inhabitants of ancient Egypt were members of what is referred to as the black, Cushite race who had entered the land as they expanded in their geographical space from the their birthplace in upper Nile Oromia, the surrounding Cushite river valleys and tropical fields. It was among these ancient people of Africa and Asia that classical technology advanced, old world science and cosmology originated, international trade and commerce was first developed, which was the by-product of international contacts, exchange of ideas and cultural practices that laid the foundations of the prime civilisations of the ancient world. Cushite Africa and also of the Middle East and West Asia was the key and most responsible to ancient civilisations and African history. It must also be known that there were no such geographical names, demarcations and continental classification at that time. As a whole, Cushite occupied this region; there was the kernel and the centre of the globe, the planet earth, and the universe. African history is out of stratum until ancient Cushites looked up on as a distinct African/ Asian nations. The Nile river, it tributes, Awash, Baro and Shebele or Juba, etc., played a major role in the relationship of Cushite to the nations in North, South and East Africa. The outer land Savannah, Nile, other Oromian rivers with it Adenian ecology were great cultural highways on which elements of civilisation came into and out of inner North East Africa. After expansions, there was also an offshoot, a graft, differentiation, branching out, internal separation, semi-independence and again interactions, interdependence and co-existence of the common folks. Cushites from the original home made their relationships with the people of their descendants in the South, the North, East and the West, which was as both good, and bad, depending on the period and the regime in power they formed and put in place in the autonomous regions. Cushite Egypt first became an organised autonomous nation in about 6000 B.C. In the Third Dynasty (5345-5307 B.C.) when Egypt had an earnest pharaoh named Zoser and Zoser, in turn, had for his chief counsellor and minister, an effulgent grand named Imhotep (whose name means ‘he who cometh in peace”). Imhotep constructed the famous step pyramid of Sakkarah near Memphis. The building techniques used in the facilitation of this pyramid revolutionised the architecture of the ancient world (Clarke, 1995). Of course, Independent Egypt was not the original home of these ancient technology. However, it was an extension, expansion, advancement and the technological cycle of the Upper Nile Oromia, Nubia, Beja, Agau and other Cushites. Ideas, systems, technologies and products were invented, tested and proved in upper Nile then expanded and adopted elsewhere in the entire Cush regions and beyond. . Bernal (1987, pp. 14-15) has identified strict cultural and linguistic similarities among all the people around the Mediterranean. He further attests that it was south of the Mediterranean and west to the Red Sea’s classical civilisation that give way to the respective north and east. Cushite African agriculture of the upper Nile expanded in the 9th and 8th century millennia BC and pioneering the 8th and 7th of the Indo-Hittite. Egyptian civilisation is Cushite and is clearly based on the rich pre-dynastic cultures of Upper Egypt, Nubia and upper Nile, whose Cushite African and Oromian origin is uncontested and obvious. Of course, Cushite Egypt gave the world some of the greatest personalities in the history of mankind. In this regard, Imhotep was extraordinary discernible. In ancient history of Egypt, no individual left a downright and deeper indentation than Imhotep. He was possibly the world’s first mult-genuis. He was the real originator of new medicine at the time. He revolutionised an architect of the stone building, after which the Pyramids were modelled. He became a deity and later a universal God of Medicine, whose images charmed the Temple of Imhotep, humanity’s earliest hospital. To it came sufferers from the entire world for prayer, peace, and restorative. Imhotep lived and established his eminence as a curative at the court of King Zoser of the Third Dynasty about 5345-5307 B.C. (Duncan, 1932). When the Cushite civilisation through Egypt afar crossed the Mediterranean to become the foundation of what we think of as Greek culture, the teachings of Imhotep were absorbed along with the axioms of other great Cushite African teachers. When Greek civilisation became consequential in the Mediterranean area, the Greeks coveted the world to ponder they were the originators of everything in its totality. They terminated to acknowledge their liability to Imhotep and other great Cushites. Imhotep was forgotten for thousands of years, and Hippocrates, a mythical posture of two thousand years latter, became known as the father of medicine. Regarding to Imhotep’s influence in Rome, Gerald Massey, noted poet, archaeologist, and philologist, says that the early Christians cherished him as one with Christ (Massey, 1907). It should be understood that, while the achievements of Cushite Egypt were one of the best, these are not the only achievements that Cushite Africans can claim. The Nubians, upper Nile, central and eastern Cushites (the Oromo, Agau, Somalia, Afar, etc) were continue to develop many aspects of civilisation independent of Cushite Egyptian interactions. These nations and states gave as much to Egypt as Egypt give to them in terms of trade, ideas and technology as well. There was also a considerable Cushite dominion on what later became Europe in the period preceding Christian era. Cushites played a major role in formative development of both Christianity and Islam. Both the Holly Bible and the Holly Quran moral texts are originated from the Oromo and other Cushite oral and moral principles, beliefs, creeds and teachings. There is a common believe and understanding that Abraham, a seminal prophet, believer and recipient of a single and eternal God was from Central Cush of present Upper Nile Oromia. The Oromos believed in a single and eternal God, Black God (Waaqa Guri’acha) also Blue God according to some scholars who translated the oral history. Waaqa also Ka. While the Oromian faith, social structure and policies were the prime and the origins of all, Judaism, Christianity, and Islam were all the derivatives and originated from the Black God. Waaqayyoo in Oromo is the original, the single, the omnipotent, the prime and the greatest of all the great religions. All aspects of the present day Christian churches were developed in Cushites. One of the more notable of Cushite contributions to the early church was monasticism. Monasticism, in essence, is organised life in common, especially for religious purposes. The home of a monastic society is called a monastery or a convent. Christian monasticism probably began with the hermits of Cushite Egypt and Palestine about the time when Christianity was established as a licit religion (Clarke, 1995). Oral tradition and Arabian records confirm that Bilal, a tall, gaunt, black, bushy-haired, Oromo, was the first High Priest and treasurer of the Mohammedan empire. After Mohamet himself, the great religion, which today numbers upwards of half a billion souls, may be said to have began with Bilal. He was honoured to be the Prophet’s first neophyte. Bilal was one of the many Cushites who concurred in the founding of Islam and later made proud names for themselves in the Islamic nations and expansions. Europe was sluggishing in her Dark Ages at a time when Cushite Africa and Asia were relishing a Golden Age. In this non-European world of Africa and Asian, Cushites built and enjoyed an age of advancement in technology before a period of internal withdrawal and isolation that favoured the Europeans to move a head of them. For more than a thousand years the Cushites were in the ‘Age of Grandeur’ but the second rise of Europe, internal strife, slave trade and colonialism brought the age of catastrophic tragedy, abase and declivity. The early Cushites made spears to hunt with, stone knives to cut with, the bola, with which to catch birds and animals, the blow-gun, the hammer, the stone axe, canoes and paddles, bags and buckets, poles for carrying things, bows and arrows. The bola, stone knives, paddles, spears, harpoons, bows and arrows, bow-guns, the hammer and the axe- all of them invented first by Cushites – were the start of man’s use of power. The present’s cannon, long-range missiles, ship propellers, automatic hammers, gas engines, and even meat cleavers and upholstery tack hammers have the roots of their development in the early Cushite use of (Clarke, 1995). Cushite offered humans the earliest machine. It was the fire stick. With it, man could have fire any time. With it, a campfire could be set up almost any place. With it, the early Africans could roast food. Every time we light a match, every time we take a bath in water heated by gas, every time we cook a meal in a gas-heated oven, our use of fire simply continues a process started by early Cushites: the control of fire. Of course, those early Cushite was the first to invent how to make a thatched hut. They had to be the first because for hundreds of thousand of years they were the only people on earth. They discovered coarse basket making and weaving and how to make a watertight pot of clay hardened in a fire. In the cold weather, they found that the skins of beasts they had killed would keep them warm. They even skin covers for their feet. It was from their first effort much later clothing and shoes developed. Humanity owes the early Cushites much and even much more (Clarke, 1995). The Cushites dociled animals. They used digging sticks to obtain plant roots that could be consumed. They discovered grain as a food, how to store it and prepare it. They learnt about the fermentation of certain foods and liquids left in containers. Thus, all mankind owes to Cushites including the dog that gives companionship and protection, the cereals we eat at break-fast-time, the fermented liquids that many people drink, the woven articles of clothing we wear and the blankets that keep us warm at night, the pottery in which we bake or boil food, and even the very process (now so simple) of boiling water- a process we use every time we boil an egg, or make spaghetti, or cook corned beef. Canoes made it possible for man to travel further and farther from his early home. Over many centuries, canoes went down Baro, the Nile and the Congo and up many smaller rivers and streams. It was in this pattern that the early Cushite civilisation was advanced. From the blowgun of antiquated Cushite, there come next, in later ages, many gadget based on its standard. Some of these are: the bellows, bamboo air pumps, the rifle, the pistol, the revolver, the automatic, the machine gun- and even those industrial guns that puff grains. Modern Scientists certain that by about 3000 B.C., the Cushite farmers in the Nile Valley were growing wheat and barely, cultivating millet, sorghum, and yams. Around 1500 B.C. new crops farming were developed: – banana, sugar cane, and coconut trees and later coffee. The cultivation of bananas and coffees in particular spread rapidly which are suited to tropical forest conditions. Cushites had also domesticated pigs, donkeys, horses, chickens, ducks, and geese, etc. (Greenblatt, 1992). The agricultural revolution brought about a gradual increase in population. Then another development helped expand population still more. The technique of smelting iron innovated by Cushites. Iron working start and then advanced in the Nile valley and then started to spread to other parts of Africa and from who, by way of Egypt and Asian Minor, this art made its way into Europe and the rest of Old World. Iron greatly improved the efficiency of tools and weapons. Iron tools and weapons are much stronger and last longer than those made of stone or wood. Iron axes made it easier to chop tropical trees and clear land for farming. Iron sickles made harvest easier. Iron hoes and other farm tools helped farmers cultivate land more easily. Iron-tipped spears meant more meat. The new technologies boosted the Cushite economy; they increased food production that enabled more people to survive. In addition, iron objects became valuable items in Cushite trade and commercial activities. With his simple bellows and a charcoal fire the Cushite blacksmith reduced the ore that is found in many parts of the region and forged implements of great usefulness and beauty. In general, the Iron technology was instrumental in auguring the rise and expansion of Cushite civilisation (Greenblatt, 1992). Cushite hunters many times cut up game. There still exists for evidences, drawings of animal bones, hearts and other organs. Those early drawings as a part of man’s early beginnings in the field of Anatomy. The family, the clan, the tribe, the nation, the kingdom, the state, humanity and charity all developed first in this region of the cradle of mankind. The family relationships, which we have today, were fully developed and understood then. The clan and the tribe gave group unity and strength. The nation, the common whole was first developed here. It was by this people that early religious life, beliefs, and the belief in one God, the almighty started and expanded. The first formal education of arts, science, astronomy, times and numbers (mathematics) were visual, oral and spoken tradition given in the family, during social and religious ceremonies. Parents, Medicine men, religious leaders, etc were the education heads. Ceremonial Cushite ritual dances laid the basis for many later forms of the dance. Music existed in early Cushite Among instruments used were: reed pipes, single-stringed instruments, drum, goured rattles, blocks of wood and hollow logs. Many very good Cushite artists brought paintings and sculpture into the common culture. The early Cushites made a careful study of animal life and plant life. From knowledge of animals, mankind was able to take a long step forward to cattle rising. From the knowledge of plants and how they propagate, it was possible to take a still longer step forward to agriculture. Today, science has ways of dating events of long a go. The new methods indicate that mankind has lived in Cushite Africa over two million years. In that long, long time, Cushites and people of their descent settled in other parts of Africa and the rest. Direct descents of early Cushites went Asia Minor, Arabia, India, China, Japan and East Indies. Cushites and people of Cushite descents went to Turkey, Palestine, Greece and other countries in Europe. From Gibraltar, they went into Spain, Portugal, France, England, Wales and Ireland (Clarke, 1995). Considering this information, the pre-Colombian presence of Cushite African mariners and merchants in the New World is highly conceivable and somewhat sounds. In this context, the first Africans to be brought to the New World were not in servitude and slavery, which contrary to popular creed. Tormenting references in the Spanish chronicles and other growing body of historical studies advocate that Cushites were the founders, the pioneers and first permanent settlers of America. Commanding authentication as in Bennett (1993, p. 85) cited by Leo Veiner in his work Africa and the discovery of America suggests that African traders founded Mexico long before Columbus. Hence, the Africans influences were extended from Canada in the North to the Maya, Aztec, and Inca civilisation in the South America. The Cushite civilisation is therefore the basis of Indian civilisation. Unlike the western Sudan and in Egypt, the people and nations of upper Nile had lost written records of their ancient times and medieval history. These were destroyed and burned during war of conquests. The early travellers to these areas are also mostly not yet known. Notable kingdoms, republics and states did rise in this part of Africa and did achieve a high degree of civilisation of their time. Scholarly undertakings show that Cushite Africans such as Oromos were the first in human history to invent and implement democratic institutions (e.g. Gada system or Gadaa system), democratic forms of government, elections and unwritten constitution. Democracy was first invented in upper Nile Oromia then to Athens, Greek and to the rest. It was not the other way round. Gada, an accomplishment of Oromian social genius in socio-political organisation is one of the most complex, the world wonder and by far superior to so far other humanity’s social and political imagination and civilisation. Gada in its vector of values constitutes, political institution, the power structure, governing constitution, the ideology, the religion, the moral authority, the economic and the whole way of life of the public, the collective, the social and the private individual. Gada is the social civilization of the Oromo in the Nile civilization. Gada is an atonishing and complex social evolution in human social transformation and an Oromo social perfection. In old Egyptian (Cushite, oromo) dialect it means Ka Adaa. Ka means God. Adaa (law). It means the law of God, the law of waaqa (God). It also symbolizes the dawn of not only civilization but also human freedom as civilazation. ‘Gadaa bilisummaa saaqaa.’ Orthodox historians and some archaeologists believe that the civilisation of Egypt is the oldest in the world, while others give that priority to western Asia or India. It has also been suggested that, since all these cultures possess certain points of similarity, all of them may evolve from an older common civilisation. Men of eminent scholarship have acknowledged this possibility. In this regard, Sir E.A. Wallis Budge (1934) indicated: “It would be wrong to say that the Egyptians borrowed from the Sumerians or Sumerians from Egyptians, but it may be submitted that the literati of both peoples borrowed their theological systems from common but exceedingly ancient source… This similarity between the two companies of gods is too close to being accidental.” A pioneer American Egyptologist, Breasted (1936) advanced the following views: “In both Babylonian and Egypt the convenient and basic number (360), of fundamental importance in the division of the circle, and therefore in geography, astronomy and time-measurement, had its origin in the number of days in the year in the earliest known form of the calendar. While its use seems to be older in Egypt than in Babylonian, there is no way to determine with certainty that we owe it exclusively to either of these two countries. A common origin older than either of is possible.” Sewell (1942) said that the science, which we see at the dawn of recorded history, was not science at its dawn, but represents the remnants of the science of some great and as yet untraced civilisation. Where, however, is the seat of that civilisation to be located?” A number of scholars, both ancient and modern, have come to the conclusion that the world’s first civilisation was created by the people known as Cushite (Oromian) and also known by Greeks as Punt (Burnt Faces). The Greeks argued that these people developed their dark colouration since they were adjacent to the sun than were the fairer natives of Europe. In terms of the sources of well-informed modern authority, Herodotus describes the Cushites as in Lugard (1964) as: “ The tallest, most beautiful and long-lived of the human races,’ and before Herodotus, Homer, in even more flattering language, described them as ‘ the most just of men; the favourites of gods.’ The annals of all the great early nations of Asia Minor are full of them. The Mosaic records allude to them frequently; but while they are described as the most powerful, the most just, and the most beautiful of the human race, they are constantly spoken of as black, and there seems to be no other conclusion to be drawn, than that remote period of history the leading race of the western world was the black race.” Alexander Bulatovich (2000, p.53) of Russia in his 1896-1898 travels in Oromia described the Oromo, which is akin to Herodotus’s description as fallows: “The [Oromo] physical type is very beautiful. The men are very tall, with statuesque, lean, with oblong face and a somewhat flattened skull. The features of the face are regular and beautiful…. The mouth is moderate. The lips are not thick. They have excellent even teeth; large and in some cases oblong eyes and curly hair. Their arm bones are of moderate length, shorter than the bones of Europeans, but longer than among the Amhara tribes. The feet are moderate and not turned in. The women are shorter than the men and very beautifully built. In general, they are stouter than the men, and not as lean as they. Among them one sometimes encounters very beautiful women. And their beauty does not fade as among the Abyssinians. The skin color of both men and women ranges from dark to light brown. I did not see any completely black [Oromo].” According to Homer and Herodotus, the Cushites were inhabited in the Sudan, Egypt, Arabia, Palestine, present Ethiopia, Western Asia and India. In his essay of historical analysis of ancient East Africa and ancient Middle East, roughly in the years between 500BC and 500AD. Jesse Benjamin (2001), brought to our attention that the importance of research focus on global formations, multi- and bi-directional and cultural relations, geopolitical associations, archaeology, linguistics, sociology, cosmology, production, commerce and consumption patterns of these regions. Benjamin (2001) indicates that historiographers have acknowledged and documented that the adored spices, cinnamon (qarafaa in modern Afaan Oromo) and cassia of the Mediterranean sphere produced and come from ‘Cinnamon land.’ The latter is also known in different names as ‘ The other Barbaria,’ ‘Trogodytica,’ Cush, Kush, Upper Nile. or ‘Punt’ but persistently representing the whole environs identified nowadays as the ‘Horn of African’ or that part of Oromia. These show the presence of production, consumption and commercial interactions in the regions. In line with Miller (1969), Wilding (1988), Benjamin (2001) included the Oromian pastoralism, pottery, cosmology and culture in the antiquity and old world civilisation. The identification of the Cushite Oromian civilisation with the present Abyssinia Amhara-Tigre under the name of Ethiopia made by the post civilisation Abyssinian priests translators of the Abyssinian version of the Bible in the 5th and 6th century or some other time, has been a cheating and misrepresentation of true human history. Those Abyssinians who were stealing the history were relatively recent migrant (conquerors) of the region. They occupied the present day Northern Ethiopia (central Cushitic of Agau and Oromo) long after the first human civilisation already originated and advanced in the area and spread to the rest of the world including to Arabia and Mediterranean Europe. The native residents of the region are the Cushite African people (Oromo, Agau, Somali, Sidama, Afar, Beja, Saho, etc). Ethiopian Jews (Falashas) are also Cushite Oromo and Agau who accepted Jews religion. Abyssinian tribes have fabricated their own myth and false history to claim legitimacy to the region and then established a regime truth through continuos fable story, phantom, indoctrination and falsification of the real Cushite history. Semitic immigrants did not found Aksum but the Abyssinians resettled among the Cushites cities and commercial centres in which Aksum was one and latter dominated the ruling power in this very centre of the civilisation of the central Cush. Ge’ez was invented as a language of the centre and latter used as the official language of the church and the colonising Abyssinian ruling class. Ge’ez was initially developed from the mixture of Cushitic and Greek elements that was facilitated by the Cushite trade links to the Greek world. There was also Greek resettlement in Aksum and the surrounding central Cush commercial towns with primary contacts with endogenous Cushite. The earlier rulers of Aksum and Christian converts including Ezana were Cushites. Though Ezana was the first convert from the above (the ruling class) to Christianity, he did not give up his belief in one God (Waqa) (Cushite/ black God). He was also not the first Cushite to be a Christian. In their linkages with a wider world, it is also highly likely and very logical and possible that there were Christians among the civilian Cushite trading communities who had already disseminated their new faith, as so many Oromo merchants were to do latter in the expansion of Islam. The splendid Stella, towers of solid masonry, with non-functional doors and windows at Aksum was not the earliest materialisation but it was the continuity in the manifestation of major indigenous Cushite tradition of monumental architecture in stone, which also later found expression in the rock-hewn churches of the Cushite Agau kings (see also Isichei, 1997 for some of the opinions). Abyssinians were the rulers. They were not the engineers and the builders of the stone monuments. It was the original product and brainchild of Cushite technologist. Of course, their advancement was thwarted with the unfortunate coming of the Abyssinians. Almost all of the original studies of the origin of Cushite civilisation could not penetrate far deep into regions south east to Nubia (Mereo) and could not dig out the other side of the twin, the close link and vast primary sources in present day Oromia. Though the British Museum has collected vast sources on Nubian, it has not kept on or linked any to the sister and more or less identical to the civilisation of the Oromo. For me, as native Oromo with knowledge of oral history and culture, as I observed the Nubian collection in British Museum, what they say Nubian collection is almost identical to Oromia, but in a less variety and quantity. I can say that Nubian and other Cushite civilisations were extensions (grafts) of the vast products of Oromo. I may also be enthused to the inference that the people whose manners and customs have been so thoroughly capitulated by Herodotus, Diodorus, Strabo Pliny and other were not Abyssinians and other Black people at all, but the natives of Upper Nile, Oromos, Agau, Somalis, Afar and the rest of Cushitic people of the present Horn of Africa. Sir Henry Rawlinson in his essay on the early History of Babylonian describes Oromos as the purest modern specimens of the Kushite. Thus, Oromo is Kush and Kush is Oromo. Seignobos (1910), in his scholarly works on the history of Ancient Civilisation reasoned that the first civilised natives of the Nile and Tigiris-Euphrates Valleys were a dark skinned people with short hair and prominent lips, they were called Cushites by some scholars and Hamites by others. So Cushite (Hamite) is generally recognised as the original home of human civilisation and culture both beyond and across the Red Sea. They are the original source of both the African and Asiatic (Cushitic Arabian) civilisation. Higgins in 1965 scholarly undertaking discusses: “I shall, in the course of this work, produce a number of extraordinary facts, which will be quite sufficient to prove, that a black race, in a very early times, had more influence of the affairs of the world than has been lately suspected; and I think I shall show, by some very striking circumstances yet existing, that the effects of this influence have not entirely passed away.” Baldwin in his 1869 study of Arab history expressed in his own words the following: “At the present time Arabia is inhabited by two distinct races, namely descendants of the old Adite, Kushite, …known under various appellations, and dwelling chiefly at the south, the east, and in the central parts of the country, but formerly supreme throughout the whole peninsula, and the Semitic Arabians- Mahomete’s race- found chiefly in the Hejaz and at the north. In some districts of the country these races are more or less mixed, and since the rise of Mahometanism the language of Semites, known as to us Arabic, has almost wholly suppressed the old … Kushite tongue; but the two races are very unlike in many respects, and the distinction has always been recognised by writers on Arabian ethnology. To the Kushite race belongs the purest Arabian blood, and also that great and very ancient civilisation whose ruins abound in almost every district of the country.” Poole (in Haddon, 1934) says, “Assyrians themselves are shown to have been of a very pure type of Semites, but in the Babylonians there is a sign of Kushite blood. … There is one portrait of an Elmite king on a vase found at Susa; he is painted black and thus belongs to the Kushite race.” The myths, legends, and traditions of the Sumerians point to the African Cushite as the original home of these people (see. Perry, 1923, pp. 60-61). They were also the makers of the first great civilisation in the Indus valley. Hincks, Oppert, unearthed the first Sumerian remains and Rawlinson called these people Kushites. Rawlinson in his essay on the early history of Babylonian presents that without pretending to trace up these early Babylonians to their original ethnic sources, there are certainly strong reasons for supposing them to have passed from Cushite Africa to the valley of the Euphrates shortly before the opening of the historic period: He is based on the following strong points: The system of writing, which they brought up with them, has the closest semblance with that of Egypt; in many cases in deed the two alphabets are absolutely identical. In the Biblical genealogies, while Kush and Mizrain (Egypt) are brothers, from Kush Nimrod (Babylonian) sprang. With respect to the language of ancient Babylonians, the vocabulary is absolutely Kushite, belonging to that stock of tongues, which in postscript were everywhere more or less, mixed up with Semitic languages, but of which we have with doubtless the purest existing specimens in the Mahra of Southern Arabia and the Oromo.
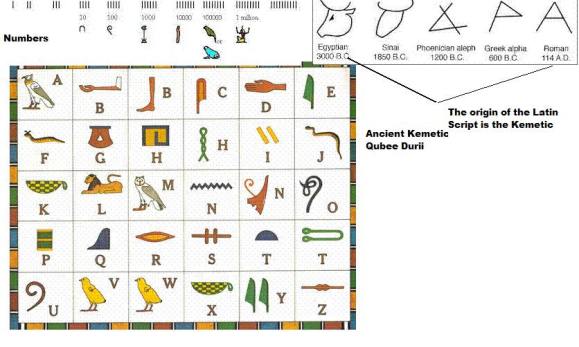
The Greek alphabet, the script of English today, is based on the Kemetic alphabet of Ancient Egypt/Kemet and the Upper Nile Valley of Ancient Africa. Ancient Egyptians called their words MDW NTR, or ‘Metu Neter,” which means divine speech. The Greeks called it, ‘hieroglyphics”- a Greek word. The etymology of hieroglyphics is sacred (hieros) carvings (glyph). The Oromos (the Kemet of modern age) called it Qubee.
Without OROMO, NO Amhara Culture & NO Amharic! – My Beta Israel & Zagwe Roots pt1 Ras Iadonis
http://gadaa.com/oduu/797/2009/09/30/ethiopia-the-story-of-oromos-irreechaa-happy-thanksgiving/
http://www.creative8studios.com/oromia/
http://bilisummaa.com/index.php?mod=article&cat=Waaqeeyfataa&article=446
http://www.americanchronicle.com/articles/view/166451
http://www.gadaa.com/culture.html
http://www.gadaa.com/Irreechaa.html http://waaqeffannaa.org/?page_id=167
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/West_Central_Oromo_language http://www.gadaa.com/language.html
http://www.voicefinfinne.org/English/Column/Galma_EOC.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hamitic#Rwanda_and_Burundii
http://oromocentre.org/oromian-story/special-report-on-the-long-history-of-north-east-africa/
African Philosophy in Ethiopia. Ethiopian Philosophical Studies II with A Memorial of Claude Sumner http://www.crvp.org/book/Series02/master-ethiopia.pdf
http://thetemplesofluxorandkarnak.wordpress.com/category/africa/
https://www.facebook.com/notes/abdi-muleta/the-story-of-irreechaa/257191284319586
CHALTU AS HELEN: AN EVERYDAY STORY OF OROMOS TRAUMATIC IDENTITY CHANGE
Chaltu as Helen: an everyday story of Oromos traumatic identity change
“Chaltu as Helen”, which is based on a novelized story of Chaltu Midhaksa, a young Oromo girl from Ada’aa Barga district, also in central Oromia.
Born to a farming family in Koftu, a small village south of Addis Ababa near Akaki, Chaltu led an exuberant childhood. Raised by her grandmother’s sister Gode, a traditional storyteller who lived over 100 years, the impressionable Chaltu mastered the history and tradition of Tulama Oromos at a very young age.
Chaltu’s captivating and fairytale like story, as retold by Tesfaye, begins when she was awarded a horse named Gurraacha as a prize for winning a Tulama history contest. Though she maybe the first and only female contestant, Chaltu won the competition by resoundingly answering eleven of the twelve questions she was asked.
Guraacha, her pride and constant companion, became Chaltu’s best friend and she took a good care of him. Gurraacha was a strong horse; his jumps were high, and Chaltu understood his pace and style.
A masterful rider and an envy to even her male contemporaries, Chaltu soon distinguished herself as bold, confident, outspoken, assertive, and courageous. For this, she quickly became a household name among the Oromo from Wajitu to Walmara, Sera to Dawara, Bacho to Cuqala, and Dire to Gimbichu, according to Tesfaye.
Chaltu traces her lineage to the Galan, one of the six clans of Tulama Oromo tribe. At the height of her fame, admirers – young and old – addressed her out of respect as “Caaltuu Warra Galaan!” – Chaltu of the Galan, and “Caaltuu Haadha Gurraacha!” – Chaltu the mother of Gurraacha.
Chaltu’s disarming beauty, elegance, charisma, and intelligence coupled with her witty personality added to her popularity. Chaltu’s tattoos from her chin to her chest, easily noticeable from her light skin, made her look like of a “Red Indian descent” (Tesfaye’s words).
As per Tesfaye’s account, there wasn’t a parent among the well-to-do Oromos of the area who did not wish Chaltu betrothed to their son. At 14, Chaltu escaped a bride-kidnapping attempt by outracing her abductors.
Chaltu’s grandfather Banti Daamo, a well-known warrior and respected elder, had a big family. Growing up in Koftu, Chaltu enjoyed being surrounded by a large network of extended family, although she was the only child for her parents.
Recognizing Chaltu’s potential, her relatives suggested that she goes to school, which was not available in the area at the time. However, fearing that she would be abducted, Chaltu’s father arranged her marriage to a man of Ada’aa family from Dire when she turned 15.
Locals likened Chaltu’s mannerism to her grandfather Banti Daamo, earning her yet another nickname as “Caaltuu warra Bantii Daamo” – Chaltu of Banti Daamo. She embraced the namesake because many saw her as an heir to Banti Daamo’s legacy, a role usually preserved for the oldest male in the family. Well-wishers blessed her: prosper like your grandparents. She embraced and proudly boasted about continuing her grandfather’s heritage calling herself Chaltu Banti Daamo.
Others began to call her Akkoo [sic] Xinnoo, drawing a comparison between Chaltu and a legendary Karrayu Oromo woman leader after whom Ankobar was named.
Chaltu’s eccentric life took on a different trajectory soon after her marriage. She could not be a good wife as the local tradition and custom demanded; she could not get along with an alcoholic husband who came home drunk and abused her.
When Chaltu threatened to dissolve the marriage, as per Oromo culture, elders intervened and advised her to tolerate and reconcile with her husband. Rebellious and nonconformist by nature, Chaltu, who’s known for challenging old biases and practices, protested “an alcoholic cannot be a husband for Banti Daamo’s daughter!”
Soon she left her husband and moved to Addis Ababa, Ethiopia’s capital, to attend formal education and start a new chapter in life.
Trouble ensues.
In Addis Ababa, her aunt Mulumebet’s family welcomed Chaltu. Like Chaltu, Mulumebet grew up in Koftu but later moved to Addis Ababa, and changed her given name from Gadise in order to ‘fit’ into the city life.
Subsequently, Mulumebet sat down with Chaltu to provide guidance and advice on urban [Amhara] ways.
“Learning the Amharic language is mandatory for your future life,” Mulumebet told Chaltu. “If you want to go to school, first you have to speak the language; in order to learn Amharic, you must stop speaking Afaan Oromo immediately; besides, your name Chaltu Midhaksa doesn’t match your beauty and elegance.”
“I wish they did not mess you up with these tattoos,” Mulumebet continued, “but there is nothing I could do about that…however, we have to give you a new name.”
Just like that, on her second day in Addis, Caaltuu warra Galaan became Helen Getachew.
Chaltu understood little of the dramatic twists in her life. She wished the conversation with her aunt were a dream. First, her name Chaltu means the better one, her tattoos beauty marks.
She quietly wondered, “what is wrong with my name and my tattoos? How can I be better off with a new name that I don’t even know what it means?”
Of course she had no answers for these perennial questions. Most of all, her new last name Getachew discomforted her. But she was given no option.
The indomitable Chaltu had a lot to learn.
A new name, new language, new family, and a whole new way of life, the way of civilized Amhara people. Chaltu mastered Amharic in a matter of weeks. Learning math was no problem either, because Chaltu grew up solving math problems through oral Oromo folktale and children’s games like Takkeen Takkitumaa.
Chaltu’s quick mastery amazed Dr. Getachew, Mulumebet’s husband. This also made her aunt proud and she decided to enroll Chaltu in an evening school. The school matched Chaltu, who’s never set foot in school, for fourth grade. In a year, she skipped a grade and was placed in sixth grade. That year Chaltu passed the national exit exam, given to all sixth graders in the country, with distinction.
But her achievements in school were clouded by a life filled with disappointments, questions, and loss of identity. Much of her troubles came from Mulumebet packaged as life advice.
“Helen darling, all our neighbors love and admire you a lot,” Mulumebet told Chaltu one Sunday morning as they made their way into the local Orthodox Church. “There is not a single person on this block who is not mesmerized by your beauty…you have a bright future ahead of you as long as you work on your Amharic and get rid of your Oromo accent…once you do that, we will find you a rich and educated husband.”
Chaltu knew Mulumebet had her best interest at heart. And as a result never questioned her counsel. But her unsolicited advises centered mostly on erasing Chaltu’s fond childhood memories and making her lose touch with Oromummaa – and essentially become an Amhara.
Chaltu spent most of her free time babysitting Mulumebet’s children, aged 6 and 8. She took care of them and the kids loved her. One day, while the parents were away, lost in her own thoughts, Chaltu repeatedly sang her favorite Atetee – Oromo women’s song of fertility – in front of the kids.
That night, to Chaltu’s wild surprise, the boys performed the song for their parents at the dinner table. Stunned by the revelation, Mulumebet went ballistic and shouted, “Are you teaching my children witchcraft?”
Mulumebet continued, “Don’t you ever dare do such a thing in this house again. I told you to forget everything you do not need. Helen, let me tell you for the last time, everything you knew from Koftu is now erased…forget it all! No Irreechaa, no Waaree, no Okolee, no Ibsaa, No Atetee, and no Wadaajaa.”
Amused by his wife’s dramatic reaction, Getachew inquired, “what does the song mean, Helen?” Chaltu told him she could not explain it in Amharic. He added, “If it is indeed about witchcraft, we do not need a devil in this house…Helen, praise Jesus and his mother, Mary, from now on.”
“Wait,” Getachew continued, “did you ever go to church when you were in Koftu? What do they teach you there?”
Chaltu acknowledged that she’s been to a church but never understood the sermons, conducted in Amharic, a language foreign to her until now. “Getachew couldn’t believe his ears,” writes Tesfaye. But Getachew maintained his cool and assured Chaltu that her mistake would be forgiven.
Chaltu knew Atetee was not a witchcraft but a women’s spiritual song of fertility and safety. All Oromo women had their own Atetee.
Now in her third year since moving to Addis, Chaltu spoke fluent Amharic. But at school, in the market, and around the neighborhood, children bullied her daily. It was as if they were all given the same course on how to disgrace, intimidate, and humiliate her.
“You would have been beautiful if your name was not Chaltu,” strangers and classmates, even those who knew her only as Helen, would tell her. Others would say to Chaltu, as if in compliment, “if you were not Geja (an Amharic for uncivilized), you would actually win a beauty pageant…they messed you up with these tattoos, damn Gallas!”
Her adopted name and mastery of Amharic did not save Chaltu from discrimination, blatant racism, hate speech, and ethnic slurs. As if the loss of self was not enough, seventh grade was painfully challenging for Chaltu. One day when the students returned from recess to their assigned classes, to her classmate’s collective amusement, there was a drawing of a girl with long tattooed neck on the blackboard with a caption: Helen Nikise Gala – Helen, the tattooed Gala. Gala is a disparaging term akin to a Nigger used in reference to Oromos. As Chaltu sobbed quietly, their English teacher Tsige walked in and the students’ laughter came to a sudden halt. Tsige asked the classroom monitor to identity the insulting graffiti’s artist. No one answered. He turned to Chaltu and asked, “Helen, tell me who drew this picture?”
She replied, “I don’t know teacher, but Samson always called me Nikise Gala.”
Tsige was furious. Samson initially denied but eventually admitted fearing corporal punishment. Tsige gave Samson a lesson of a lifetime: “Helen speaks two language: her native Afaan Oromo and your language Amharic, and of course she is learning the third one. She is one of the top three students in the class. You speak one language and you ranked 41 out of 53 students. I have to speak to your parents tomorrow.”
Athletic and well-mannered, Chaltu was one of the best students in the entire school. But she could not fathom why people gossiped about her and hurled insults at her.
Banned from speaking Afaan Oromo, Chaltu could not fully express feelings like sorrow, regrets, fear and happiness in Amharic. To the extent that Mulumebet wished Chaltu would stop thinking in Oromo, in one instance, she asked Chaltu to go into her bedroom to lament the death of a relative by singing honorific praise as per Oromo custom. Chaltu’s break came one afternoon when the sport teacher began speaking to her in Afaan Oromo, for the first time in three years. She sobbed from a deep sense of loss as she uttered the words: “I am from Koftu, the daughter of Banti Daamo.” Saying those words alone, which were once a source of her pride, filled Chaltu with joy, even if for that moment.
Chaltu anxiously looked forward to her summer vacation and a much-needed visit to Koftu. But before she left, Mulumebet warned Chaltu not to speak Afaan Oromo during her stay in Koftu. Mulumebet told Chaltu, “Tell them that you forgot how to speak Afaan Oromo. If they talk to you in Oromo, respond only in Amharic. Also, tell them that you are no longer Chaltu. Your name is Helen.”
Getachew disagreed with his wife. But Chaltu knew she has to oblige. On her way to Koftu, Chaltu thought about her once golden life; the time she won Gurracha in what was only a boys’ competition, and how the entire village of Koftu sang her praises.
Her short stay in Koftu was dismal. Gurraacha was sold for 700 birr and she did not get to see him again. Chaltu’s parents were dismayed that her name was changed and that she no longer spoke their language.
A disgruntled and traumatized Chaltu returns to Addis Ababa and enrolls in 9th grade. She then marries a government official and move away from her aunt’s protective shield. The marriage ends shortly thereafter when Chaltu’s husband got caught up in a political crosshair following Derg’s downfall in 1991. Chaltu was in financial crisis. She refused an advice from acquintances to work as a prostitute.
At 24, the once vibrant Chaltu looked frail and exhausted. The regime change brought some welcome news. Chaltu was fascinated and surprised to watch TV programs in Afaan Oromo or hear concepts like “Oromo people’s liberation, the right to speak one’s own language, and that Amharas were feudalists.”
Chaltu did not fully grasp the systematic violence for which was very much a victim. She detested how she lost her values and ways. She despised Helen and what it was meant to represent. But it was also too late to get back to being Chaltu. She felt empty. She was neither Helen nor Chaltu.
She eventually left Addis for Koftu and asked her parents for forgiveness. She lived a few months hiding in her parent’s home. She avoided going to the market and public squares.
In a rare sign of recovery from her trauma, Chaltu briefly dated a college student who was in Koftu for a winter vacation. When he left, Chaltu lapsed back into her self-imposed loneliness and state of depression. She barely ate and refused interacting with or talking to anyone except her mother.
One afternoon, the once celebrated Chaltu warra Galaan took a nap after a coffee break and never woke up. She was 25.
The bottom line: Fictionalized or not, Chaltu’s is a truly Oromo story. Chaltu is a single character in Tesfaye’s book but lest we forget, in imperial Ethiopia, generations of Chaltu’s had to change their names and identity in order to fit in and be “genuine Ethiopians.” Until recently, one has to wear an Amhara mask in order to be beautiful, or gain access to educational and employment opportunities.
Likewise, in the Ethiopia of today’s “freedom of expression advocates” – who allegedly sought to censor Tesfaye – it appears that a story, even a work of fiction, is fit to print only when it conforms to the much-romanticized Ethiopianist storyline.
So much has changed since Chaltu’s tragic death a little over a decade ago, yet, clearly, much remains the same in Ethiopia. Honor and glory to Oromo martyrs, whose selfless sacrifices had allowed for me to transcribe this story, the Oromo today – a whole generation of Caaltuus – are ready to own, reclaim, and tell their stories.
Try, as they might, the ever-vibrant Qubee generation will never be silenced, again.
Origins of the Afrocomb: Exhibition: Fitzwilliam Museum, Cambridge, UK; 2nd July – 3rd November
Origins of the Afro Comb: 6,000 years of culture, politics and identity
http://www.gatewayforafrica.org/event/origins-afro-comb-6000-years-culture-politics-and-identity?__utma=1.1154313457.1380212922.1382522461.1382771276.8&__utmb=1.217.9.1382772351901&__utmc=1&__utmx=-&__utmz=1.1382771276.8.5.utmcsr=royalafricansociety.us2.list-manage.com|utmccn=(referral)|utmcmd=referral|utmcct=/subscribe/confirm&__utmv=-&__utmk=134257777&utm_content=buffer9ca97&utm_source=buffer&utm_medium=facebook&utm_campaign=Buffer
Even today, a significant number of mainstream Egyptologists, anthropologists, historians and Hollywood moviemakers continue to deny African people’s role in humankind’s first and greatest civilization in ancient Egypt. This whitewashing of history negatively impacts Black people and our image in the world. There remains a vital need to correct the misinformation of our achievements in antiquity.
Senegalese scholar Dr. Cheikh Anta Diop (1923-1986) dedicated his life to scientifically challenging Eurocentric and Arab-centric views of precolonial African culture, specifically those that suggested the ancient civilization of Egypt did not have its origins in Black Africa.
Since some people continue to ignore the overwhelming evidence that indicates ancient Egypt was built, ruled, and populated by dark-skinned African people, Atlanta Blackstar will highlight 10 of the ways Diop proved the ancient Egyptians were Black.
Physical Anthropology Evidence
Based on his review of scientific literature, Diop concluded that most of the skeletons and skulls of the ancient Egyptians clearly indicate they were Negroid people with features very similar to those of modern Black Nubians and other people of the Upper Nile and East Africa. He called attention to studies that included examinations of skulls from the predynastic period (6000 B.C.) that showed a greater percentage of Black characteristics than any other type.
From this information, Diop reasoned that a Black race existed in Egypt at that time and did not migrate at a later stage as some previous theories had suggested.
”’ኦሮሞና ኦሮሚያ”’
የኦሮሞ ሕዝብ መሠረተ አመጣጥ ከኩሽ ቤተሰብ የሚመደብ ነዉ። በቆዳ ቀለሙና በአካላዊ አቋሙ ከሃሜቲክ እስከ ናይሎቲክ ያጣቀሰ ዝርያ ያለዉ ሕዝብ መሆኑ ታሪክ አረጋግጦታል። በሰሜን ምሥራቅ አፍሪካ ከሚኖሩ ህዝቦች ጋር በብዙ መልኩ ተመሳሳይነት ያለዉ ነዉ። በዚህ ክልል የሚኖሩ ሕዝቦች ታሪክ መመዝገብ ከጀመረበት ጊዜ አንስቶ የኩሽ ቋንቋ ተናጋሪ መሆናቸዉ ተረጋግጧል።
ኦሮሞ የኩሽ ቋንቋ ተናጋሪ ብቻ አይደለም። ይልቁንም ይህ ሕዝብ በአህጉረ- አፍሪካ ቀደሚ ዜጋ ሆነዉ ከኖሩት ሕዝቦች መካከል የመጀመሪያ መሆኑ ይታወቃል። በዚህ የረጅም ዘመናት ታሪኩ ውስጥ ለሥልጣኔዉ የሚሆኑ ባህሎችን እስከማዳበር ደርሷል። ሊንች እና ሮቢንስ የሚባሉ ሁለት የዉጭ ምሁራን ሰሜናዊ ኬኒያ በተገኘዉ ጥንታዊ አምድ ላይ ከትጻፈዉ መረጃ በመነሳት ኦሮሞዎች በ3000 ዓመተ-ዓለም አካባቢ የራሳቸዉ የሆነ የቀን መቁጠሪያ እንደነበራቸዉ አረጋግጠዋል። ይህም ሕዝቡ በዚሁ ክልል ለመኖሩ አንዱ ተጨባጭ ማስረጃ ነው።
ከሊንች እና ሮቢንሰም ሌላ ፕራዉቲ እና ሮሴንፊልድ የተባሉ የታሪክ ሊቃዉንት “Historical Dictionary of Ethiopia” ኢንዲሁም ባትስ : “The Abyssinian Difficulty” በተባሉ ሥራዎቻቸው ; <> በማለት ይገልጻሉ።
የኦሮሞ ሕዝብ የምስራቅ አፍርካ (የአፍርካ ቀንድ) ቀዳሚ ቤተኛ ስለመሆኑ አያሌ ማስረጃዎች ኣሉ። ስለዚሁ ጉዳይ ታሪካዊ ሰናዶች በብዛት ይገኛሉ። አባ ባህሬይ የተባሉ የአማራ ብሄር ተወላጅ የጋላ ታሪክ ብለው በሲዳሞና ከፋ ዉስጥ በመዘዋዋር ስላ ኦሮሞ በፃፉት መጽሃፍ በጥላቻ የተሞሉና ትክክል ያል ሆኑ ታሪኮችን ለማሳተም በቅተዋል። ክራፍ በ 1842 ፥ ፍት በ1913 በክልሉ በመዘዋወር ኦሮሞ በምስራቅ አፍርካ ከሁሉም የላቀ ስፍት ያለዉ ሀገር ባለቤት መሆኑን አረጋግጠዋል ።
ከ1850 በፊት ዲ. አባደ ቤክ፥ እስንባርገር ኢንዲሁም ክራፍ የተባሉ አዉሮፓዊያን ዘጎች የኦሮሞን ሕዝብ ፖለቲካዊ ፥ ባህላዊና ማህበራዊ አኗኗር ሥራዓት በማጥናት ለዉጭዉ ዓለም አስተዋዉቀወል። ከዚያም ወዲህ በተለይ ከ 18ኛው መቶ ክፍለ ዘመንና በኋላም ኦሮሚያ በአፄ ምንልክ ተወርራ የኢኮኖሚና የፖለቲካ ሥራዓቷን ከመነጠቋ በፊት ሲቺ የተባለ ኢጣሊያዊ እንዲሁም በሬሊ ; እና ሶሌይሌት የተባሉ የፈረንሳይ ዜጎች በኦሮሚያ ህዝብ ፖለቲኮ-ባህላዊ; ኢኮኖሚያዊና ማህበራዊ ታሪኮች ላይ ያተኮሩ ሥራዎችን አዘጋጅተዉ ለአንባቢያን አቅርበዋል።
ታሪካዊ ጥናቶች አንደሚያረጋግጡት ኦሮሞና ኢትዮጵያ ከ16ኛዉ እስከ 19ኛው መቶ ክፍለ ዘመን አንዱም ሌላዉን አሸንፎ በ ቁጥጥሩ ሥር ሳያደርግ ጎን ለጎን ሆነው ሲዋጉ መቆየታቸው ሆሎኮምብ እና ሲሳይ ኢብሳ በ 1900፥ ፕሮ. መሐመድ ሐሰን በ 1990፥ ፕሮ. አሰፋ ጃላታ በ 1990፥ መሐመድ አሊ በ 1989፥ ሌቪን በ 1965 ፥ ገዳ መልባ በ 1978… ሥራዎቻቸዉ ዉስጥ በስፋት አቅርበዋል። እንዲሁም ጄስማን የተባሉ ጸሐፊ ከ50 ዓመታት በፊት ባሳተሙት መጽሓፍ ከአፄ ምንልክ የደቡብ ወረራ በፊት የነበረችዉ ኢትዮጵያ በሰሜን ከፍታዎች አካባቢ መሆኑን ከመግለጻቸዉም በላይ ማአከሏም በሰሜን ትግራይ ፥ በጌምድር ፥ ላስታና ወሎ ፥ በመሃል ጉራጌ ፥ በ ደቡብ ሸዋ ነው ያሉት ከላይ የተጠቀሱ ምሁራን ያ ቀረቡኣቸዉን ቁም ነገሮች በተጨባጭ መልክኣ ምድራዊ ገጽታ የሚያረጋግጥ ሆኗል።
ጥንታዊቷ አበሲኒያ ቀደም ብሎ በተጠቀሱት ክልሎች ላይ ብቻ የተወሰንች ለመሆኗ አፄ ቴዎድሮስ ኢየሩሳሌም ሳሙኤል ጎባ ለተባሉ የእንግሊዝ ጳጳስ በጻፉት ድብዳቤ ውስጥ ከጠቀሱትም ቁም ነገር መገንዘብ ይቻላል። እችሳቸውም:-
Copyright © The Oromianeconomist 2014 and Oromia Quarterly 1997-2014, all rights are reserved. Disclaimer.
Related articles
https://www.facebook.com/notes/abdi-muleta/the-story-of-irreechaa/257191284319586
The Ethiopian Apartheid Policy on Oromo at Irreecha Festival (oromocentre.org)
This Month in Recorded Oromo History – Highlights (bilisummaaa.wordpress.com)
Invitation to Oromo National Thanksgiving Day (oromocentre.org)
The Wonderful Cushitic Oromia: Naming is Identifying (freedomfororomo.wordpress.com)
“Little Oromia” celebrates all week long in Minneapolis By Michele St. Martin (oromoland.wordpress.com)
Meroitic language is one of the most controversial ancient languages but one of the few having advanced writing systems. Some classify it Asian, European, non-African, Semitic,or ‘unclassified’. This paper contends Meroe, similar to their Cushitic friends, are left victims of preconceived ideas based on an entirely argument from silence, an hegemonic epistemology that elevates a single perspective and silences other(s). This paper, thus,comparatively analyzes Meroitic and Old Nubian lexical and grammatical items with corresponding Oromo, a Cushitic family which,
a Cushitic family which,vocabulary possibly the Ancientlanguage of the Nile Valley and/or Horn of Africa. Meroitic and Old Nubian lexical, grammatical and epigraphic data were collected from secondary sources by Meroitic researchers. Oromo corpora are obtained both from classical and modern descriptions and native-speakers. Results indicate Oromo lexemes show significant level of cognates with not only Meroitic and Old Nubian, but also with the Ancient Egyptian to their northern part.
Yaa Maaraam furootu gahee
Waliin nu Gahee
Emmoo yaa obbolee emmoo
Maaram is believed to be the divinity of women. Maaram was created by Waaqa and
addressed as haadha boor (the mother of ocean). I think this is to indicate that Maaram
came to the Oromo from outside. The Oromo believe that Mooram is the mother of a
child. The Oromo women perform traditional ceremonies in respect of Maaram. It is
believed that Maaram will help barren women to beget a child, and help pregnant
women to give birth to a child. When a woman gives birth to a child Oromo women will
gather and ululate (say ilili ilili). They also prepare porridge, and splash butter. It is
normal for the Oromo to sacrifice an animal during this ceremony. Moreover, Maaram
is worshipped for the health of the environment, animals, human beings and crops.
The Oromo Qoolluu leaders pray to Maaram every two weeks for the continuation of
offspring of humans. Maaram has her own ritual house. Ritual goods include Jaaloo
(earthen caldron), and Qoloo (traditional shirt). It has also madabii (raised platform of
Earth). The dancing ceremony is performed on Tuesdays, Thursdays,. and Saturdays.Some writers have explained the nature of Ateetee and Maaram. Knutsson states that the names Ateetee and Maaram are used interchangeably for the same kind of being (Kmitsson 1967,55). Daniel states that the various songs of Ateetee imply that “[a]teete is a ceremony prepared for Ayyolee, Maaram and Waaqa as thanksgiving by those who have children and a lamentation by the barren women” (Daniel 1984, 111). Bartels, however, questioned this assertion. To the Oromo of Western Matcha, Ateetee is the name of the ritual in which Maaram is invoked (Bartels 1983). Baxter (1979) had similar observation concerning the belief of the Arsi Oromo. For Cerulli, Ateetee is conceived as the goddess of fecundity (Cerulli 1922,127; Harris 1968,50).
– http://www.ossrea.net/publications/images/stories/ossrea/ssrr-19-p-3.pdf
In the traditional Oromo society, women played distinct roles through an institution called the Siiqqee (a symbolic decorated stick given to all women by their mothers upon marriage). This is an exclusively women’s solidarity institution sanctioned by tradition and respected by society. It is a sort of sorority that provides women with channels to participate in village councils, and a cultural vehicle to mobilize en masse against violence and abuse. Infringement of certain rights that women enjoy is regarded as an attack on human rights. In the event of violation of their rights, women take out the Siiqqee and mobilize to fight for the respect of rights, and for any perpetrator of abuse to be tried by society. The use of Siiqqee draws an enormous religious, ritual and moral authority and in the pursuit of peace and social tranquility. According to tradition peace is not merely the absence of war, but a constant state of unity and cooperation among the people as well as harmony with God and nature, with the power to bless or curse. Historically, women as a sector of society were designated as strangers and excluded from the Gadaa structures and rituals, but, they stuck together through the Siiqqee counting on one another within this common sorority. –http://oromowomensinternationalconferenceonline.com/general-information.html
http://www.slideshare.net/chalihundu/oromo-peoplehood-historical-and-cultural-overview
http://trace.tennessee.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1080&context=utk_socopubs
http://zelalemkibret.files.wordpress.com/2013/07/jos-volume-4-numbers-12-1997.pdf
In Oromo mythology, the divinity for motherhood and fecundity is Ateetee or Maaram. Maaram or Ateetee is invoked and praised on birth-rituals. In addition, women prepare a feast and invoke Her, praise Her kindness so that they could be fertile, healthy, prosperous, and happy (Bartles, 1990,124; Cerulli 1917, 127, Tilahun Gamta, 2004,101)
Atoomaa hardhoo Maarami!
Maa mukoofna yee!
Yaa Maaram yaa Maaramii,
Wallaalaaf araarami.
Yaa Maaram, yaa kuullee koo,
Kottu taa’i fuullee koo.
Ciniinsuu afaa butuu
Miixuu dagalee butuu
Da’anii mucaa butuu
Iddoo ciniinsuu kee tii
Guddeen kun kan kee ti.
Yaa deessuu waalluu kobe,
Maaramtu boroo gonfe,
Dhirsatu balbalaa kolfe.
Yaa dhabduu waalluu moojoo
Dhirsatu aaree guungume,
Maaramtu boroo sokkee.
Utuun Balasiin ta’e,
Balas Boongaa ta’e,
Dhabaadhaaf mirgan kenna;
ittiin haa doorsifatu.
Utuun Maaramiin ta’e,
Maaram giiftii ta’e,
Dhabduudhaaf ilman kenna,
Dhirsa haadoorsifattu.
Yaa Maaram, yaa Maaramee
Dhabduudhaaf araarami mee.
Yaa Maaram godeettii koo
Yaa dhiiga toleettii koo
Yaa Maaram marmaartuu koo
Yaa hiika gargaartuu koo.
Aayyoleen walii lama
Tokkoo ishee carii gamaa
Tokko ishee asii kana.
Akka abbaa fardaa beeka
Irraangadee kaachisa
Akka abbaa warraa beeka
Niiti deessuu caalchisa
Gaangoo jedhee na cabsee
Gindoo saa nabaachisa
Yaa maaram hundaaf giiftii
Rakkoo kiyya naaf hiiki
Yookaan ilmaa naa kennii,
Beekaattan moggaafadha
Yookaan durba naa kennii
Beektuuttin moggaafadha
Yookaan dua naa kennii
Waayeekoon obbaafadhaa.
Get-together, for today is Maaram
Let us rejoice, throw away the boredom!
O Maaram, O dear Maaram,
Reconcile, with us who lack wisdom.
Maaram with beautiful eyes, O Maaram,
Have a sit, in front of me, please come!
When in pain, the mattress one clutches
When in labour, the wall one clutches
After delivery, a baby one snatches!
In return for your labour pain
Here, the little one is your gain.
O prolific woman, your clothes smell bad,
But Maaram has adorned your backyard,
The husband laughs from the front yard.
O sterile woman, with beautiful dress
Your husband furiously grumbles,
For your backyard, Maaram avoids.
If I were Balas,
That Balas of Boongaa,
To a bad-shooter his trophies I give;
So he could boast about it with relief.
If I were Maaram,
Our great lady Maaram,
A son I would give to the sterile woman,
So she could intimidate her man.
O Maaram, my dear Maaram
Be merciful to the childless.
O Maaram, with beauty and grace
You have revered blood in your face
O Maaram, you are my commuter [between me and God]
My parturifacient mother.
Two kinds of mothers are there
One is far across the river [The biological one]
The other one is the one here. [Maaram]
I know a rider’s thought and will
He gallops down the hill
I know a husband’s thought
He loves the prolific wife the most;
He equates me to a mule, dry and bare
and makes me carry his ploughshare.
O Maaram every women’s’ queen
Resolve this problem for me
Either grant me a baby boy
I call him “he the wise”
Either grant me a baby girl
I call her “she the wise”
Or either give me death
So I could get done with my worries.
The following stanza is taken from a birth song:
Odoshaa gofaa ka’u
Sareen agartee laata?
Agartee nyaattee laata?
Dhabduu ishee mucaaf boossu,
Yeelalaa fayyaaf boowu,
Adeemsa mirgaa boowuu
Maareen agartee laata?
Agartee laattee laata?
Ililleen Waaqa akka
Ililcheen Waaqiin kadha;
Gabaa shaqaxxuu faaqi
Anoo sagadduu Waaqi!
Loome qoraan karaa
Yomiree wal agarraa?
Bor guyyaa afaan waaree
Loonee wal agarra.
Garbuu kaballaa tokko
Manteessuun akaawwatte
Kan maseente ittiin horte
Kan deesse lakkaawwatte.
Deessuun akka naan jette
Mucaa koo hinargin jette
Diinqa koo hindarbin jette.
Maali yoon diinqa shee darbee?
Maali yoon mucaa shees argee?
Mucaa sheef argaan laadha
Garaa koof marqaan nyaadha
Jabbisheetu gola miti
Mucasaheen dhora miti.
Yaa dhabduu anaa nyaatu
Ulfooftee gumaa hin nyaannee
Deesse gumaata hindhugne.
Dhagaa kakatta guutuu
Rarra’etu wal baachise
Dhabduun dawuu hinjibbine
Maaramtu wal caalchise
Yaa deessuu waalluu qobe
Ayyaanni boroo gonfe.
Yaa dhabduu waalluu moojoo
Ayyaanni boroo sokke.
Yaa dhabduu masoo dhirsa
Dhirsatu dhaanu hawwee.
Yaa saree eegee dabbasaa
Kan quufee Waaqiin darbata
Kan Maaram namaa gootu
Haati ofii namaa hingootu.
Sibiila mutaa gootee
Kan djiiga mucaa gootee.
Baddaan qullubbii hinqabu
Muree laga dhaabbata
Kan kee dhukkubbii hinqabu
Turtee nama yaadattaa.
Araarfanne yaa maaram
Sirraa deenyee.
Gadi jedheen xaafii haamaa
Ol jedheen Waaqiin waama
An old horse’s rise from the stable,
I wonder if dogs have seen it and been able?
To have eaten it, and then did settle?
Cry of a baby-longing childles
Lament of a health-longing patient
A trophy-longing hunter’s plight
I wonder if Maaree have seen?
If She has seen and granted!
Ululation for Waaqa is a must
I ululate and beseech Waaqa;
Market of the taxing tanner
I am Waaqa’s earnest prayer!
The Loomee firewood of the street
When do you think we could meet?
Tomorrow, around mid-day
We will meet slipping away.
A handful of barley
That a widow parched and eat
the sterile prospered with it
the prolific counted it. [To equally divide.]
You know what the prolific said?
“Do not see my baby.” she said
“Do not enter my inner-room” she said.
What if I enter her inner-room?
What if I see her baby?
To her baby, I give a gift
To my stomach, porridge I eat.
No calf is kept in her inner-room,
She thinks I pine her child, I presume.
What a pity for the sterile lady
She could not get pregnant and eat a hunk of meat
She could not deliver and have showers of gift.
Abundance of rock and escarpment
Is hanging and piling up
The sterile did not hate giving birth
It is Maaram that un equalizes.
The prolific with smelly skirt
Her backyard is full of spirit.
But, the childless in a pretty skirt
Her backyard is devoid of spirit.
The sterile, the husband’s name-sake
The husband wishes to punish her.
O dog with a hairy tail
The over-fed hurls at Waaqa
The favour Maaram does for one
One’s own mother would not do.
She turned iron to needles
She turned blood to a baby that toddles.
The high land does not have onion
They cut and plant in the valley;
Your delay is not offensive
for you compensate gradually.
Reconciliation with you, O Maaram
You gave us deliverance.
I bow down and harvest xaafi [food plant]
I rise up and invoke Waaqi

Hoga iyya Siiqqee
Ilmaan hidda Horoo,
Guchuma baattee siida Ateetee
Siiqqeen iyyite seenaaf godaante
Safuuf nagaa waaqa tokkichaan dursa
Na ofkolchaa iyya Siiqqeefan tumsaa
Godaana siiqqeefan imimman robsa!
Safuu! Hoga iyya Siiqqeef
kan mandiisu akka bakakkaa
Safuu! Godaana faana Siiqqeef
Seenaa hin duune, kan hin qabne fakkii fi akka!
Uggum! Hoga iyya Siiqqeef
Iyya eenyummaa – diroon fufe gumaaf birmatu
Uggum! Godaana faana Siiqqeef
Adeemsa seenaa – qaraan-qara hin dhaabbatu
Hoo dhommoqxes Siiqqeen hin cabdu
Harooressa hin haanxoftu – gogdee hin baddu
Ni latti akka coqorsaa – jilbeeffattee dhukaan riqxee
Ni lalisti akka saardoo – margee leensa diroon cobxee
Ni daraarti akka keelloo – kuusaa aadaan booka naqxee
Sarara ulumaa Siiqqeen hareeroo
Hormata eenyummaa seenaa iyya Horoo
Duudhaa ganamaa irkoo fi utubaa boroo
Jandoo baaxii galma suuqa sororoo
Siiqqeen hin baddu dagaleen Gadaa
Kanaaf iyyatti – qabattee guchuuma aadaa!
Kan Waaqni mildhate Ayyaantuun eebbaa
Eenyummaaf birmadhu jamaan kaabaa fi kibbaa
Hoga dabarsaa, bahaa fi lixaa seenaa utubaa
Seenaa iyya Siiqqeef goonni dhiiga roobaa!
Kuusaa Oromummaa fi Hooda Ayyaantuu
Bir’uu eenyummaaf Siiqqeef birmatu!
Gadaan quufaa fi gabbina
Gabbisi ya Waaq, keenniif humna!
Humna Siiqqee kan hin cabne
Humna Gadaa kan hin dabne
Humna Oromummaa kan hin banne
Dilbii- Kuusaa kan hin dhumne
Seenaa boonsaa eenyummaa abdanne!
Gadaan gabbina Siiqqeen hareeroo
Gabbisi yaa waaq nurraa cabsi roorroo!
http://waaqeffannaa.org/iyya-siiqqee/
Oromo and Greek based Democracies
By Ibsaa Guutama
This article is for those who did not have the opportunity to know how democracy evolved in human society. Democracy is only one type of government supposedly based on the will of the masses. There had been other types of government like monarchy or aristocracy, dictatorship or autocracy and totalitarian. One can find overlapping characters in all these. So what ever form we may talk about we have to expect element of one in the other. For much, democracy is an ideal type of government but not all proclaimed democracies are fully pro-people. Here the writer is trying to introduce the essence of both Western and Oromo democracy in an easy way. For those who are well versed in theory and practice of democracy this is an opportunity to enrich this work for the benefit of the youth. In particular the young generation that is showing pride in its historic past from oral tradition if armed with the facts may show more interest and start to inquire about it. To prepare the following information in addition to oral tradition and experience this writer was exposed to, the books: Gadaa and Oromo Demokrasii by Asmirom Laggasaa, The Oromo by De Salviac as translated by Qannoon, Folk Litrature by Ceruuli, Aadaa Booranaa by Ton Leus, Ethiopia through Russian Eyes by Bulatovich and Wikiipedia from internet were refered to.
Short note on Western Democracy
Democracy is a term frequently heard from lips of everyone to express equality, justice and liberty in one word. There are no governments that do not claim to follow democratic principles in their governance. Even totalitarian states call themselves “democratic republics” (probably with exception of fascism) in spite of flagrant violation of their subjects’ rights. Just like true democrats they talk about the inviolability of people’s and human rights and respect for the rule of law and fair and free election. They claim that it is to protect these rights on behalf of the masses when they take what are inhuman actions for others. Their founding documents are full of borrowed phrases from ideal democracies. Democratic governmental structures are adopted minus their functions from different countries.
Democratic models many emulate are American governmental structure with its system of separation of powers. The functions of legislature, executive and judiciary are separated into three branches in such a way that one can check on excesses of the other to maintain the balance of power. The executive or President and the legislative or members of Congress are elected directly by the people. Members of the Supreme Court are nominated by the president and endorsed by the legislature for life. The other models are Parliamentary Democracy where the executive is elected by the legislature. Those can be its members or non elected persons that are answerable to it. Britain and European governments fall under this. They have mainly different styles of organization. Still others are traditional rulers blended with modern jargons.
All these claim their objective to be safeguarding peoples’ democratic interests. The term democracy is a legacy of ancient Greek city state, Athens. It is derived from Greek demokratia which means government of the people (“demos”, people, and “kratos”, power). In this aspect “people” for Athens includes only male citizens above 20 years of age. That does not include women, children under 20, those not born in the city state and slaves.
In the city state all those qualified had the right to be present at meetings and participate in deliberations directly. That is why it is now referred to as direct democracy. After many modifications it has reached the present level of modern Western democracy. Here people elect representatives that participate in deliberations on its behalf. The two methods of electing representatives are plurality and proportional voting systems. In the first one with the highest vote is elected even if one represents minority of voters. The second shares votes in proportion of the votes parties got in overall election. Those are the features of modern indirect democracy. In both not all electorates are represented.
Now in most cases men and women above certain age have the right to vote depending on the law of each democratic country. The right to vote for women was achieved, for example, for Switzerland in 1971 on federal level and 1990 at Canton levels. It took a long time and a relentless struggle to attain universal suffrage. Though all accept these basics of democracy the structure and function of elected offices are not yet standardized and methods of elections fall short of including every voter’s voices. For example if hundred people vote for three persons and two of them got thirty votes each and the third one gets forty he/she wins the whole thing. That leaves 60 persons unrepresented. Proportional representation may improve this but cannot totally correct it. Here seats are divided in proportion to votes parties got overall.
For African countries democracy was imposed on them by departing colonial masters that keep on insisting to this day not to abandon it even if it was a fake one. Africans did not participate to construct a government relevant to their culture and tradition. Even those who later wanted to introduce amendments tried to mix the various world systems instead of looking into their own history and tradition and make it reflect national personality or psyche. As copy and eclectic as it is, it is understood only by elites who themselves are copies of colonial culture.
They rule the way they wanted, constitutions are only window dressings. On the other hand the West had modified the concept of democracy in such a way that it fits their particular national needs not as it was practiced by Athenians or any other pioneer democracies. Therefore there is no one common blueprint for it.
Had it not excluded a segment of the population Athenian democracy could have been an ideal one where the concern of every member is taken care of. Much has been tried to approximate that but the world did not yet achieve flawless democracy. Abraham Lincoln’s famous Gettysburg Address “Government of the people, by the people for the people shall not perish from the earth.” reflects that aspiration. The question to be answered is who are the people that influence decisions, are they really the people or oligarchs? Though the ideal is not yet achieved there are those that had come nearer and worth emulating. Had Oromo democracy been able to answer that question?
Be as it may there are certain basics that underlie every governance of those that claim to be democratic. Principles like equality, freedom, fair and free election; rule of law and respect for people’s and individual rights run through all of them. Even dictators and totalitarian government claim to apply these principles in their own way. Thus these are universally accepted principles of governance though malpractice is rampant in so many countries. Ethiopian rulers had tried to adopt constitutionalism under pressure against their established tradition. The emperor had instituted a semblance of Westminster parliament without political parties. His successor (Darg) had one party state. The next (Wayyaanee) is a pseudo multiparty system but only its party is destined to win.
Be him the last emperor or the two dictators after him used democratic phraseology to cover up their core authoritarian values. Their inherited autocratic practices could not go away. The Habashaa in most part of their own history were ruled by forces that come through coup d’états violently or outlaws overthrowing the preceding government. That was so before they formed the empire and remained so even after it. All the three came to power overthrowing their predecessors. The first two staged coup d’états the third was an outlaw.
It was not consensus but brut force that kept that highland kingdom together under one crown. Democracy assumes one man one vote in a fair and free election that should be carried out periodically. Democracy is the rule of majority. Who ever gets most of the votes comes to power. In numbers they are the minority in the empire and are scared of others outnumbering them at the ballot box. They have no confidence of winning an election by strength of their platform and performance. Therefore they believe that many opportunities would be at stake if they really change from the old ways bowing down for democratic principles. The situation makes the rulers greedy, self centered, chauvinistic and paranoid that they believe only in their own ways and wisdom and are not permeable to new possibilities. They do not believe that even their own people would elect them in a democratic election. That is why human right abuse became their trade mark.
Brief note on Gadaa Democracy
When one discusses Gadaa it would be preposterous to claim understanding its depth and breadth. It was a highly complicated and sophisticated societal system to be attributed only to few generations. That it has a background of ancient civilizations can be deduced from organization of society, its legal system and patterns of knowledge it emanates. For this reason what this article presents is only a simplistic superficial aspect of it, which yet could give a clue to its democratic legacy. Leaving aside procedures, rituals and the regalia what interests us here is the legal and democratic principles enshrined in it. To discover the truth of it much effort is needed from nationals that so far considered it to be just one among the age grade initiation systems found in so many societies. They have to erase all they learned about the Oromo in colonial schools and start unraveling the truth about this so far neglected great African nation.
Gadaa was an all encompassing national system where by every male of all ages had roles to play in groups based on peerage. Accordinglly all institutions in society were managed by elected bodies that decide in counsel. Though all activities in general fall under the Gadaa system, it was more visible in its political aspect. Major divisions to be considered are the temporal and the spiritual institutions and within the temporal one the social and the political functions. Gadaa is temporal while Qaalluu is spiritual. It is said that the Qaalluu office used to assist in Gadaa operations like elections. But sovereignty is vested in Gadaa Assembly. Therefore Qaalluu as an institution does not interfere in running political affairs of the country. That means Gadaa was secular. Here we are more interested in Gadaa secular democracy. The social and political aspect of the spiritual institution may worth following for its historical and academic significance. There are several Oromoo that follow traditional religion to this day.
Gadaa was practiced by the Oromo people from time immemorial. In social aspect male members of society are grouped into age grade “hiriyaa” (peer) system. To simplify, these were Dabbalee from 1-8 years, Foollee or Gaammee 9-24 and Qondaala or Kuusaa 25-33, Raaba didiqqaa 30-38, Raaba Doorii, 38-46 Luba 46-54 and Yuba 55-78 and gadamoojjii or jaarsa above 78 (taken from different regions practice for convenience). Each member of a society had rites to pass through. At each grade there were roles to be played and training to go through.
Activity of a hiriyaa group starts from cradle to calf herding, to different hurdles of fitness that include military training to ruling and counseling the country. It is from these hiriyaa groups that members of national leadership evolve and gradually become Luba, members of the Gadaa ruling group. These leaders in most cases had been leaders of hiriyaa group from the beginning. Women, non naturalized aliens (kan luba hin bahin) and artisans were not included in Gadaa power sharing process.
One Gadaa period is eight years. At the end of that period there used to be great feast. That ceremonial feast was called “Buttaa”. Buttaa also served as measurement of time. To know someone’s age one asks “how many Buttaa did you eat?” All those who were born during the eight years tell the same age, one, two, three etc. Buttaa. From that a wise man could tell to which hiriyaa group or Gadaa party one belonged. Five buttaa are slain in one Gadaa cycle of forty years. Those born into each Gadaa are hiriyaa (peers) irrespective of up to eight years possible differences. A boy born at the beginning of the eight years and one born on Buttaa day after eight years are considered to have eaten one Buttaa.
On the political side society is divided into Gadaa of five parties. Members in each Gadaa party were recruited from their own generational age grades. Each Gadaa has a role to play in the political life of the nation depending on the time and level in the Gadaa tier. The oldest group is the Yuba. It is composed of person whose members were in power in previous times. Next is Luba, the ruling party. Below that is the Itmakoo or Raba Doorii (these may have other names with different tribes) juniors that lead in defense and nation building. The next group follows the foot steps of their seniors and engages in different aspects of society appropriate for their ages. Each hiriyaa group maintains close relationship and prepare themselves for the next stage of partisan responsibility. They all elect their leaders. Those at the bottom of the ladder are the dabbalee to whose raising society gives much attention. It is there that the basis of Oromummaa is laid down and hunting for generational leaders start.
At any one period there are three Gadaa levels that engage is serious party work and has conventions or yaa’a. The bottom one is Raabaa Doorii a group that is preparing to take power after eight years (from), the middle one is the Gadaa in power Luba and the last one is the one that leaves office, Yuba. Each Gadaa comes to power after a cycle of forty years. Since there is a party in waiting to replace the other no party can stay in power for more than eight years. No crisis can be obstacle to transfer Baallii for there is a ready made leadership. To transfer Baallii means to transfer authority. As symbol of authority the old Abbaa Gada hands over to the incoming ostrich feather that was in his custody. Each Gadaa proclaims its own constitution and laws. Therefore there is no stagnation in waiting for cumbersome methods of amendments. Even if there is no article to be changed the past law is formally made null and void and proclaimed again as new. The five Gadaa had set names or are called after their leaders.
The highest Assembly of the nation is Caffee or Gumii. The Caffee sits under shade of an Odaa tree. The General Assembly includes all members of the ruling party and any such persons that want to attend it. In this way it is a representative indirect democracy with some elements of direct democracy. Living Abbaa Gadaas and the Yuba can also participate in the assembly. Abbaa Gadaa or Abbaa Bokkuu is the head of the Caffee and the chief executive as well. There is a case where their were two heads of Caffee, one ritual head called Abbaa Bokkuu and another elected head, Abbaa Gadaa. The Luba usually consults “raagaa” wise man or philosopher on the future or consequences of certain decisions. But the raagaa has no power to avert a decision.
In addition to mentioned institutions there are several others that should not escape our attention. For example the institution of clan elders which are hereditary have no place in the Gadaa structure but has important role in organizing and guiding the tribe. Members of Gadaa were recruited (nominated) from tribes they lead. They have ritual symbols and roles to play in cursing and blessing. When Gadaa is the national leadership these ones are tribal ones. It was from among these ones that the colonizers embraced and recruited as agents for all their grassroots activities. In tribal protocol the eldest of the clans is called or seated first. Since tribal structures have already been rendered obsolete it has no nationwide political relevance in modern setting. There is also the Siiqqee institution that gives women social and political authority to some degree. In principle this can be integrated into any modern adaptations.
For the Oromo rights like equality, freedom, fair and free election; rule of law and respect for people’s and individual rights, respect and protection for environment and wild life are inbuilt qualities of Gadaa democracy. All human beings are equal; no one is above the law; discrimination because of origin, color or economic status etc is unjust. Respect for human rights, freedom of expression that are not safuu or morally repulsive, freedom of movement and association are protected by law. Elected officials are loved and respected as long as they serve the people whole heartedly and with the highest morale standard. An incompetent and corrupt official can be removed from office by the assembly before the expiry of his term of office. In meetings it was preferred if decisions were reached by consensus. Each member of a meeting or assembly has the right of veto to halt a discussion. Once decisions were reached all are required to acclaim and the law becomes sacred.
Gadaa Assembly combines executive, legislative and judiciary powers. Gadaa here is to mean the ruling class as well as the eight years of their rule. Leaders of current Gadaa are called Luba. The outgoing Gadaa which participates as advisors and judges are called Yuba. The Yuba group includes two previous Yuba. Though all powers and responsibility lie with the Luba, Yuba and all living Abbaa Gadaas had also roles to play in matters of law and checking on excesses of Luba and had great influence on all political matters. Full retirement comes three Gadaa after they leave office. From thence they are called gadamoojjii or jarsaa. Another hiriyaa group that is active during a Gadaa period is the Itmakoo or Raaba Doorii with defense as their major activity with their eye on the bokkuu when the time comes.
In Oromo society there was a tendency of the weak to form alliance against the strong. For example grandparents and grandchildren ally against parents. In the same way it is logical for Raabaa Doorii to ally against the strongest institution of the land, Luba. In that way power of Luba can be checked before it gets corrupted and become abusive.
The chief Luba is the Abbaa Bokkuu or Abbaa Gadaa (Hayyuu Fiixee). In places he has two deputies one having greater power than the other. The executive power is held by Salgee, the top nine Luba or six in some places. Those were elites elected by the people for eight years with Abbaa Gadaa as their leader. Committees were usually formed at different levels for different functions. Prerogatives of decision making at each level is known. There will always be consultation before decisions are taken. They were it is believed, those frequent meetings to make seera (law, legislation) that gave rise to Amaara legal term “seeraa” to mean conspiracy.
Abbaa Bokkuu implements what is decided by Salgee. Abbaa Bokkuu’s role as a chief is defined by law. Thus he has internal constraint imposed on him by peers and external ones by Yuba and Raaba Doorii and Caffee periodic assembly that is chaired by Abbaa Seera who is a well respected past Abbaa Gadaa. The limitation of office term of only eight years for a party is by it self a reason not to get corrupted lest face humiliation with no chance of reelection. Thus Gadaa democratic system was a well balanced system with inbuilt checks and balance mechanism. The Abbaa Gadaa and Luba had assistances called makala (Makkala). Makala kan be compulsory service to Gadaa offices.
Military functions are assigned to Raaba Doorii by law and tradition. But Abbaa Gadaa was commander in chief and only Caffee can declare war. Commanders are appointed by Abbaa Gadaa for each engagement. After a campaign is over the person went back to his normal duties.
But lack of efficient communication and contingent law enforcement mechanism had given rise for Abbaa Duulaas to defy tradition starting in the course of the 16th century.
Some cardinal points of Gadaa system
Is there any point that modern society discard from these? So far we have tried simplistic approach to uncover old Gadaa practice. Gadaa was more inclusive in its membership than Greek City state democracy. It involves every member of society to equally participate in all activity of the nation according to generations. All male nationals are grouped into generational hiriyaa and play roles society assigned for them. For this reason the Gadaa system involves all in the process of managing a society. Each division stays in the age grade for eight years before it is initiated into the next level. Probably except kids under nine all elect their leaders through electoral process. Gadaa was a representative democracy with some elements of direct democracy. Anyone that can travel to Caffee Assembly can participate in its deliberations and express ones opinion. That gives it semblance of direct democracy. Gadaa was practiced when Qaalluu institution had significant role in Oromo society and the nation was at a different level of economic and technological development than the present. Taking these variations into account let us see if there are principles that we could salvage for new democratic Oromiyaa.
To summarize, the people are sovereign; representative system mixed with direct democracy were practiced; rulers were elected for a limited term of only eight years; citizens had the right to elect and be elected according to their ages; no one was above the law; people can recall their representative; humans, animals and nature are protected by law; the welfare of children was concern of all members of society; their was majority rule but by making decision by consensus minority views were protected; all human being were equal, ill treatment was abhorred; right to assemble and freedom of expression were protected; right to engage in any trade was protected; right to travel were granted; right to worship was recognized and discrimination based on race, age, gender and economic status are forbidden. There was inbuilt check and balance system in the political process but not so spelled out.
Now, that we have seen a brief introduction to western and ancient Oromo Gadaa democracy, let us try if we can come out with a fitting system for reorganizing modern Oromiya. The system of dividing and managing society into generations is not different from modern world school systems. Children learn what is assigned them according to peerage, “preschool, kindergarten, primary, secondary, college”. This is not far from what they call “dabbalee, Foollee, Gaammee, Raaba etc.” Existing political parties recruit members from this school system. But the Oromo as different as they are, had something to add and their own outlook. Oromo see the system in interrelation with all other societal activities. To pass from one stage to the other are rights of all citizens not of particular classes.
Probably it would be essential to revise certain things and see how they may serve modern society better. Instead of collectively saying Oromo youth association if one says association of Foollee, Gaammee, Raaba etc it will help to mobilize in unison generation that under stand each other better. It may also give better opportunity to develop future leadership for society. In the past stages in the Gadaa were seen from fathers’ point. For this reason the age at which one has to produce a child was determined. If one is born before that it was bad omen. Now all children should be treated equally and age has to be considered from childrens point. So, age should not be calculated by butta and father’s Gadaa grade, but the exact date of a child’s birth. All those excluded to participate in gadaa activities and elections must now be included to make true that all humanbeing are eqal. This is only the skeleton otherwise social functions require deeper research. During the period of Abbaa Gadaa there was only one Qaalluu, now they are numerous (in addition to those of other religions). In the past we go for pilgrimage only to Abbaa Muudaa now we crossed the sea and added Mecca and Jerusalem etc. After all, what do you think? This is a big challenge for Oromoo intellectuals. It may require liberating ones mind from the shackles of foreign influences to appreciate what we had. Gadaa is never obsolete but may need refurbishing. Go and make research before responding.
Let us get prepared to be ourselves and show the world that Gadaa still dwells in our minds and body. This will not be difficult for one who has pride in Oromummaa.
Honor and glory for the fallen heroines and heroes; liberty equality and freedom for the living and nagaa and araaraa for the Ayyaanaa of our fore parents!
Ibsaa Guutama
July 2011
http://gubirmans.com/Oromo%20and%20Greek%20based%20Democracies.html
…The presence of the aged, both men and women who attired in traditional costumes, and carrying ritual sticks—bokkuu and siiqqee—the symbols of power and justice of the gadaa system decorated the march which reflected the authentic Oromo tradition. This authenticity is articulated not only in the words spoken by the elders and sung by the artists but also expressed in the peacefulness of the gathering of millions of people. Oromo nationalism is reviving and thriving in the fertile soil of rich symbolic cultural resources that have come to the open since the 1990s. The array of national symbols such as the odaa tree which decorate the costumes worn by men, women and children, the siiqqee, the bokkuu and other pre-colonial pan-Oromo symbols carried by men and women at the festival represent and reinforce the pride of the nation and unite the multitude gathered for the festival through a common imagery of shared memories, myths and values—in other words the shared structures of feeling.
http://maddawalaabuupress.blogspot.co.uk/2012/11/oromo-freedom-from-what-and-for-what.html
Related Article:
by Rundaasaa Asheetee Hundee
is the principle of deep moral honor and accountability that was fostered by Waaqayyo fearing people of Oromia. “Yoon maqe, Waaqni na arga” is the principle rooted in each Oromo proven to be worthy of wholesomeness, to have virtue, and love other. These type of people have a desire to understand and live by traditional values.
Young Oromo children often spoke about the fundamental principle that telling the truth, respecting nature, being trustworthy, and standing for the right thing is natural to human beings. As an Oromo, we were taught these values and it made us women and men of such noble character.
Not only our characters were shaped by Safuu Oromo, even the process of Seera tumu (law making) was inspired by this principle and the Gadaa system was framed on the basis of Safuu. Basically then, Safuu is the principle of restoration of human dignity in a significant way. Because of Safuu, Birmadummaa and honesty is expected from each Oromo so that we all can live virtuous life of divine purposes.
When the Oromo people lived according to the Gadaa system, they dominated the horn of Africa and established their republic, and the Oromoo Foollee turned into statesmen and defended the norm of Gadaa governance. Because they believed in being honest, true, benevolent and virtuous in doing good to humanity, they demanded no money for their work and time. They worked on their farms but served their country as abbaa Seeraa, abbaa Alangaa, abbaa Caffee, abbaa Bokku and as Hadha sinqee etc..
Because of Safuu, the Oromos are inspired to respect nature and committed to deal justly with humankind! That’s why we are indebted to freedom-loving individuals everywhere who had the integrity necessary to build the foundations of human societies upon safuu’s fundamental moral values. Only in an atmosphere of freedom and trust could values like honesty and integrity truly flourish.
Safuu Oromo therefore is an expectation that people must rise above self-interest and act in the public interest with wisdom and courage both on the national and the local political scene.
One reason for the decline of Safuu in Oromia to day is that people invented new standards that constantly changes and undependable moral conduct. As a result, individuals define good and evil as being adjustable according to each situation but doing so is in direct contrast to the Safuu standard.
The vast majority of so called educated Oromos speak or think based on this mindset where right and wrong are calculated to either remain neutral or to be liked by others at the expenses of own value, the Safuu. In the process, our people lost their ancestral knowledge of what is right and what is wrong and went astray by longings for luxury and leisure that they think will be found in the western world style of living and thinking.
The devastation that comes from such fraudulent life style and self misrepresentation is immeasurable. It leads to a false belief that they can worship anything they want following the rules they set for themselves.
However, the continued survival of a free and open society is dependent upon a high degree of divinely inspired values and moral conduct (safuu), as stated by the Oromo Ayaantus. People must have trust in their institutions and in their leaders. Hence, a great need today is for leadership that exemplifies truth, honesty, and decency in both public and private life.
Honesty is not only the best policy, it is the only policy according to Safuu Oromo.
There are several things we can do to develop SAFUU.
Desire It (Fedhii Safuu horadhu)
Live honest life (hin Maqin)
Be Humble (Fayaalessa ta’i)
Study (Qu’adhu)
Search and ponder on ideas (Yaada xiinxali)
Love nature ( Umaa jaaladhu)
Read @ http://advocacy4oromia.org/home/safuu-the-oromo-moral-value-and-doctrine/
http://ayyaantuu.com/horn-of-africa-news/oromia/safuu-the-oromo-moral-value-and-doctrine/
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | ||